5 Cooking Techniques For Faster Meal Prep

When you’re tired from work, school, or other activities, you probably don’t have enough time or energy to work in the kitchen, cooking complicated dishes!

Photos By: Adobe Stock Images
Because of this, you might want to consider learning essential cooking techniques that could help you prep and cook your meals faster than before.
Unfortunately, not all techniques can speed up meal preparation, particularly when it comes to braising, stewing, and reverse searing. Unlike other basic cooking techniques, these require more time, and they’re more difficult to process. For example, braising meats in red wine may require reduction and thorough cooking in the oven, which makes it extremely time-consuming.
However, the key to faster meal preparation and cooking isn’t just the techniques but how the heat is transferred into the food, such as how meat gets heated in a frying pan. If the heat is delivered evenly, it can cook your food much faster, cutting your cooking time in half.
Without further ado, here are the most efficient cooking techniques you need to know to quicken your meal preparation for stress-free eating time.
Sautéing
Sautéing is one of the most popular cooking methods used in many cultures all over the world. Usually, it’s done with only two kitchen essentials: a frying pan and a touch of oil. It can be used to cook most ingredients, such as seafood, meats, vegetables, and poultry, in a quick and easy way.
Also, sautéing uses direct heat to brown and sear different ingredients perfectly. This browning reaction (caramelization) is an indication of complex flavors and aromas being released in the food. Thus, it doesn’t just cook your meals faster, but it also gives you a pleasant dining experience.
Sautéing can also be a primary step when braising or stewing meats. In this process, the mirepoix (a mix of three different vegetables, usually onions, carrots, and celery) is sautéed before the other ingredients. But for the most part, it’s a great way to have shorter cooking time, especially when preparing meals for family and guests.
Don’t know what to sauté? You could start with ingredients that are quick to cook, such as seafood and vegetables. You could also cook your favorite steaks with this technique in just a few minutes.
Blanching
If you prefer crispy and partially cooked vegetables, you might want to try blanching them. Blanching is a cooking technique where an ingredient (usually a vegetable) is submerged in boiling water for a few minutes and then shocked in ice water to stop the cooking process. However, if you want to eat the veggies right after blanching, you may skip the shocking process.
If you’re looking for food to blanch, you may go for green beans, asparagus, and broccoli, all of which are flavorful and delicious, even if they’re partially cooked. For additional flavor, you may season them with salt and pepper after blanching, or you may season the water with salt in advance.
Grilling
Grilling is one of the easiest and fastest ways to cook food. It uses both direct and indirect heat to cook all kinds of meats and vegetables thoroughly in a matter of minutes.
However, prepping a grill can be time-consuming, especially if it’s a charcoal grill. Luckily, there are easy ways to do this without exerting too much effort. You can do this with a grill pan on top of your stove, a gas-operated grill, or an electric grill.
Also, most ingredients to be grilled don’t need many spices or other ingredients to amplify their flavor. Usually, salt, pepper, and good-quality olive oil are enough to elevate the food’s texture, juiciness, and characteristics.
For an even faster meal prep with grilling, choose ingredients that can be cooked in a matter of minutes. A good choice would be chicken, seafood, or vegetables. Red meat may also cook faster on a grill, but make sure you don’t slice them too thick so you can let the insides cook thoroughly.
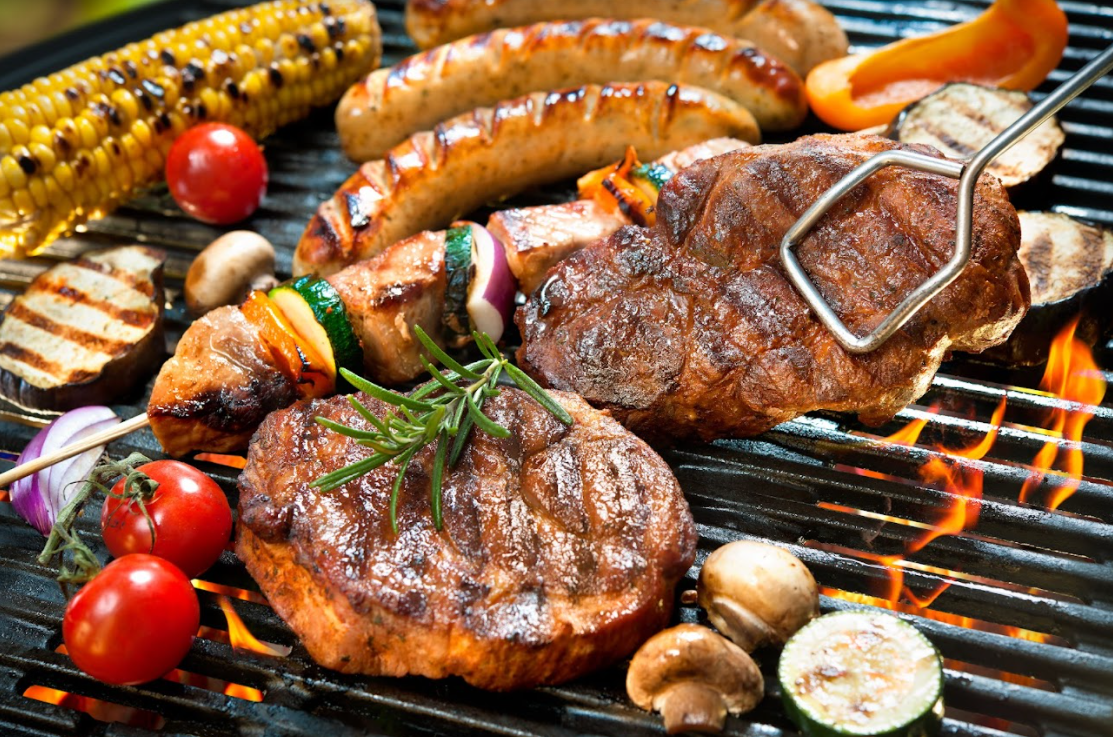

Stir-Frying
Stir-frying and sautéing are similar in many cases, but the former is much faster when it comes to cooking food. Unlike sautéing, stir-frying uses intense heat and constant motion (stirring and tossing) to cook the food as quickly as possible. Usually, stir-frying involves using a rounded wok to easily shake up the food directly over high heat.
Also, it’s worth noting that butter is not applicable when stir-frying. Unlike other oils, butter burns easily because of the milk solids that quickly caramelize. But if you want to add the richness and creaminess of butter to your dishes, you may use clarified butter instead. Clarified butter has no milk solids and can withstand higher temperatures without burning, like other oils.
Roasting
Roasting may seem to take longer than other cooking techniques, but it’s worth mentioning because it’s pretty easy to do. Usually, roasting is done in an oven under controlled temperature conditions. It uses heat circulation to cook the food evenly without the food having to be constantly stirred.
When roasting, there are only two essential things you have to do: prepare the main ingredients (meat or vegetables) and season them with salt and pepper or a good-quality oil. After that, you can place it inside a preheated oven and let it cook, depending on the recipe.
Roasting typically takes 15 minutes or longer, depending on the type and size of the meat or vegetables you’re cooking. However, it allows you to exert minimal effort and do what you need to do while the food is cooking in the oven.
Need an idea of what to roast? You may go for asparagus seasoned with salt and pepper and drizzled with olive oil. Or you could chop up some quarter leg of a chicken and do the same prep you did for your veggies.
Final Word
Quick and easy meal prep is essential for busy people who might not have the time to prepare many dishes for a group or for themselves. If that’s the case for you, you might want to consider the five cooking techniques discussed above. These will allow you to prepare your meals in just a couple of minutes. However, you should also consider other factors that could affect and prolong the cooking process, such as the amount of the ingredients and the size of the dish you’re planning to cook.