The Necessity of Flat Roofing Systems for Commercial Properties
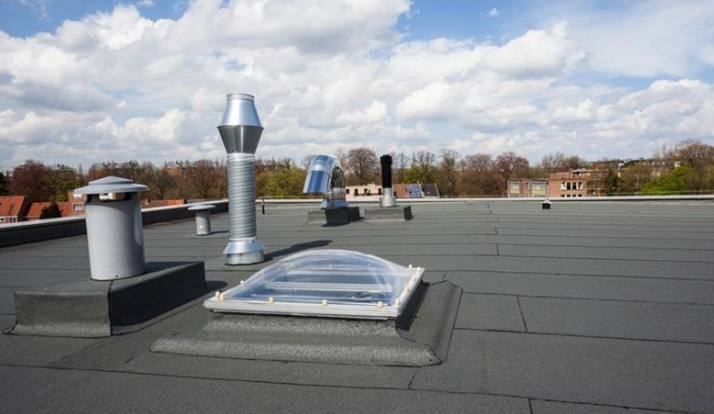

Commercial buildings usually demand a compromise on the cost, strength, and functionality of roofing. Flat roofing structures are one of the most popular constructions applied to warehouses, office buildings, shopping complexes, and industrial facilities.
They are popular because they can cover extensive spaces effectively, bear heavy loads such as HVAC units and carry energy-saving techs such as solar panels. In the case of property owners, it is important to learn about the available flat roofing types, their advantages and their long-term effects so as to make a good investment.
Why Flat Roofs Suit Commercial Properties
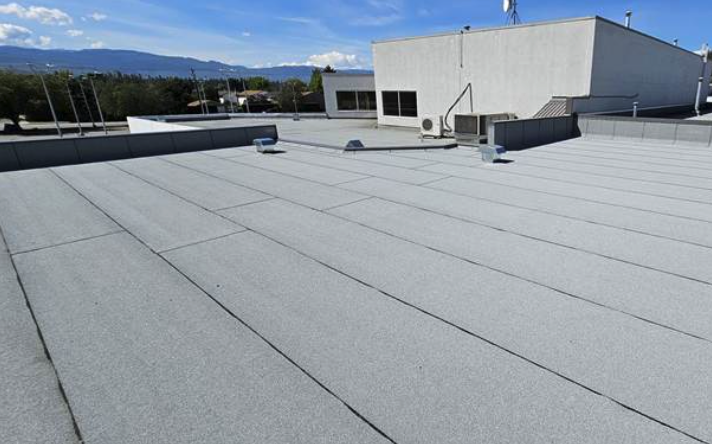
The flat roofs are not totally flat as they are developed with a slight gradient to facilitate drainage. This structural design simplifies them and is cheaper to construct over large commercial areas than pitched ones.
Their horizontal terrain has practical advantages of housing rooftop amenities, a place in which mechanical equipment can be placed, as well as providing space that may be used as a green roof, or recreational purposes, in certain city developments.
The other benefit is accessibility. The flat roofs are easier and safer to maintain, repair and clean than the pitched ones. This availability makes it less time consuming when repairs are done and minor problems are identified before they can develop into serious problems. To commercial operators, the simplicity in inspection means that they get predictable maintenance and this may lead to low costs. You can contact SW commercial roofing services to take care of the installation for you!
Built-up Roofing Systems
For many years, built-up roofing has been a reliable option. Bitumen and reinforcing textiles are laid in multiple layers, with gravel or protective coatings applied on top. As a result, the roof is long-lasting, weather-resistant, and capable of withstanding heavy traffic.
Though it may require a lot of manual labor to install, BUR’s multi-layer design makes it an ideal waterproofing material. In addition, the method uses asphalt heating, which emits pollutants and is thus less eco-friendly than alternative systems. But for homeowners looking for a long-lasting option, BUR is still a solid pick.
Upgraded Bitumen Systems
An improved version of BUR, modified bitumen roofs are more adaptable and long-lasting than their predecessors. Membranes made of asphalt and polymers are able to withstand mechanical stress and temperature fluctuations.
A variety of installation methods are available, such as those that include a torch, cold application, or self-adhesion. In areas where there is a large variation in seasonal temperatures, modified bitumen is favored by property owners due to its resistance to severe weather. Additionally, it offers a strong waterproofing layer without necessitating the same amount of manual labor as conventional BUR systems.
EPDM Roofing Systems
Commercial roofing frequently makes use of EPDM, or ethylene propylene diene monomer, a synthetic rubber membrane. Epdm, which comes in big rolls, is mechanically or adhesively attached to roof decks to provide a long-lasting and watertight barrier.
It is ideal for areas with a lot of sunshine because it is very resistant to weathering and UV radiation. EPDM roofs are affordable and, with maintenance, can endure for 30 years or more. Because of how easy they are to set up and fix, they are a staple for budget-conscious homeowners who value durability.
Roof Systems Made of TPO
Among the several flat roofing materials available, thermoplastic olefin (TPO) is quickly becoming a popular choice. The reflecting qualities of TPO, a single-ply membrane, greatly decrease heat absorption and increase energy efficiency, making it highly appreciated.
Heat welding creates watertight bonding at the joints of TPO sheets, making them leak-proof. Commercial buildings that are trying to lower their electricity bills over the long run have found TPO to be an attractive option due to its low price, ease of installation, and energy savings.
Roof Systems Made of PVC
An additional thermoplastic roofing material that is commonly used in areas that are exposed to chemicals, oils, or greases is polyvinyl chloride, more commonly known as PVC. Businesses like restaurants and industries can benefit greatly from its resistance to these toxins.
Reinforcing PVC membranes makes them stronger, and heat-welding their seams makes them waterproof like TPO. Due to its extended service life and simple maintenance requirements, PVC is frequently considered a beneficial investment by property owners, although being more expensive than TPO or EPDM.
Benefits of Flat Roof Systems
Commercial property owners can get a lot of benefits from flat roofing systems. In general, they are cheaper to put over long distances than pitched roofs because they need fewer materials and less complicated work. Their ease of access makes upkeep and safety better, and their adaptability helps equipment and green technologies. Many modern flat roofing materials also help save energy, either by having surfaces that reflect light and lower heat gain or by being able to work with solar panels and plants on the roof.
Flat roofs can be used on a lot of different types of commercial buildings, from warehouses to office parks, because they are easy to plan. Because it is flexible, property owners can find a solution that meets both their functional wants and their budget.
Things to Think About During Installation
To pick the right flat roofing system, you need to carefully plan ahead and talk to a professional. The climate is an important factor. Reflective membranes like TPO or PVC work well for buildings in sunny areas. On the other hand, homes in areas that get a lot of rain or snow may need systems with stronger waterproofing layers. The choice is also affected by what the building is used for.
For example, factories or restaurants might need PVC that is resistant to chemicals, while a logistics building might choose EPDM because it is cheaper.
The budget is always very important. Some systems are cheaper up front, but they may need to be serviced more often. Other systems cost more up front, but they save more energy and last longer. It’s also important to think about what you might need in the future, especially if you plan to add more solar panels or tools to your roof in the future. Learn more here.
How to Do Maintenance
Even though flat roofs are easier to take care of than pitched roofs, they still need to be maintained regularly. At least twice a year, commercial property owners should have checks done to look for holes, cracks, or seam failures. Roof drains should be free of garbage so that water doesn’t sit there and cause leaks. Keep an eye on the flashing around vents, skylights, and HVAC systems to make sure it stays in place.
Some membranes can have their life extended with protective coatings, and small fixes should be taken care of right away to keep them from getting worse. Many people who own homes sign maintenance contracts with professional roofing companies to make sure that their roofs get the care they need all the time. This can extend the roof’s life and keep them from having to pay for unexpected costs. Read more here.
Costs and Lifespan Expectations
Flat roof systems depend on the material, the mode of installation, and the building size which determines the associated cost. The built-up roofing and modified bitumen are normally durable with relatively low costs whereas the TPO and EPDM have the potential to balance the costs of installation and durability. PVC is rather costlier but provides additional chemical and energy saving.
Systems also have variable lifespan. EPDM may have up to 25 to 30 years in service, whereas TPO and PVC can service a lifetime of up to 20 or 25 years. Constructed and altered bitumen systems have a span of between 15 and 20 years although it may take more time with proper care.
When roofing is considered as an investment instead of a cost especially in the long term, this can help the property owner to make the correct decisions with respect to their financial and operational objectives.