Choosing the Right Furnace for Your Home: A Comprehensive Guide
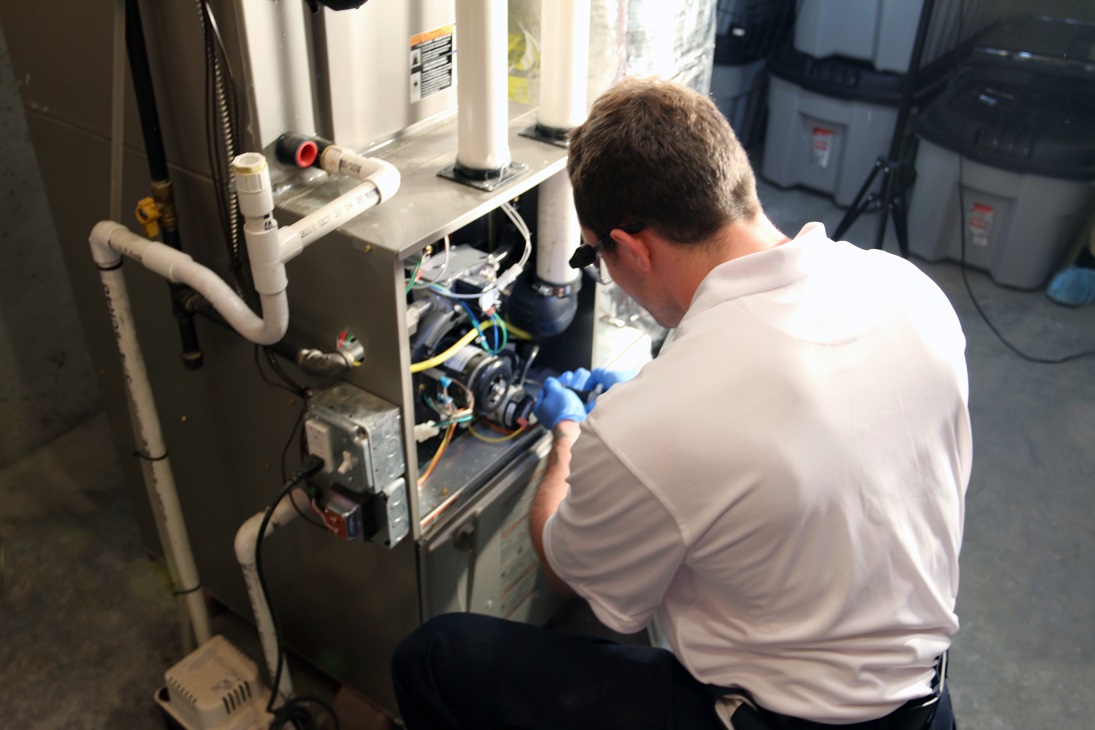

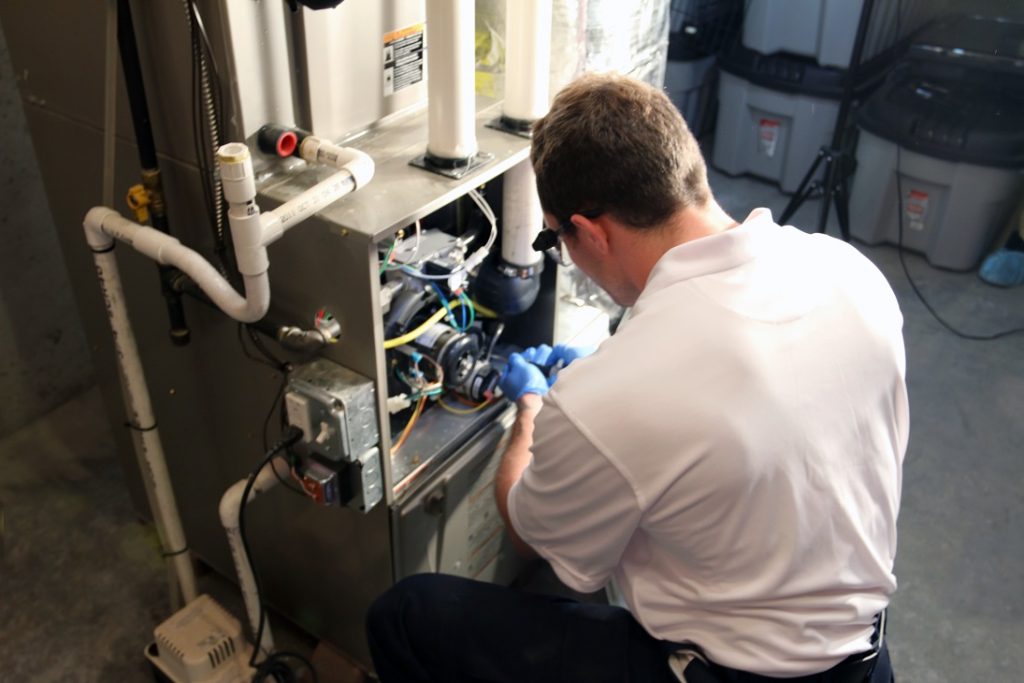
As temperatures drop and winter approaches, ensuring your home remains warm and inviting is vital. The right furnace can make all the difference in energy efficiency, comfort, and overall household expenses.
There are several factors to consider when investing in a new heating system, especially if you want to strike the perfect balance between reliable warmth and affordability. If you are preparing for a new installation or an upgrade, it’s essential to make an informed decision for your home’s long-term comfort. For expert guidance and efficient furnace installation in Brampton, professional support can simplify your decision-making process and ensure proper setup.
Understanding the key distinctions among furnace types, energy efficiency ratings, and your home’s heating requirements will help you navigate this important choice. Factors such as climate, home size, and budget directly influence your furnace’s performance and long-term costs. By exploring advanced features now available in modern heating systems and considering ongoing maintenance, you position your household for years of dependable comfort.
Whether you are replacing an old unit or buying one for a newly built home, understanding core differences and evaluating advanced furnaces will lead to smarter, more satisfactory outcomes. Prioritizing professional expertise ensures your installation matches your specific needs and maximizes your investment.
Understanding Furnace Types
Choosing the right furnace starts with understanding the four main types available. Each has distinct advantages and may suit different home layouts or local infrastructure:
- Gas Furnaces: These systems use natural gas to generate heat and are popular in regions where gas is readily accessible. They tend to be more energy efficient and cost-effective for most urban homeowners.
- Electric Furnaces: These systems are a good fit for homes without access to natural gas. While initial costs may be lower, operational efficiency is generally lower than that of gas units.
- Oil Furnaces: Less prevalent in modern homes, oil furnaces are chosen in areas where oil delivery is dependable and gas infrastructure is lacking. They usually require on-site storage tanks.
- Propane Furnaces: Like gas systems, these devices run on propane and serve properties located outside urban centers where natural gas lines do not reach.
Deciding between furnace types depends on heating requirements, budget, fuel availability, and long-term maintenance considerations.
Assessing Energy Efficiency
The energy efficiency of a furnace impacts both your utility bills and carbon footprint. Efficiency is measured by the Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE) rating, indicating the percentage of fuel converted into usable heat. High-efficiency furnaces typically have AFUE ratings of 90% or higher, meaning the majority of the fuel is converted to heat for your home rather than lost in exhaust.
While higher-rated furnaces tend to come with a higher initial price tag, the investment often pays off in reduced monthly utility bills and better overall environmental performance. Checking for ENERGY STAR®-certified units is a simple way to identify top-performing, energy-efficient models. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, upgrading from an older, low-efficiency furnace to a high-efficiency model can save hundreds of dollars in annual energy costs.
Determining the Right Size
The capacity of a furnace must align with your home’s heating demands. An oversized unit could cycle on and off too frequently, undermining energy efficiency and straining components over time. Conversely, an undersized system may never adequately warm your space during colder periods. To establish the ideal size, HVAC experts perform load calculations that factor in home square footage, ceiling height, window insulation, and even local climate.
Accurate sizing leads to greater longevity, fewer repairs, and lower utility bills, making it worth your time to consult a professional for the assessment. For a more thorough understanding of sizing approaches, Energy Star explains the importance of proper HVAC sizing.
Considering Climate and Location
Your region’s climate plays a pivotal role in choosing a furnace. In colder zones, a high-efficiency, high-output furnace may be necessary to handle extended sub-zero temperatures. Meanwhile, homes in more moderate climates might not need as robust a heating system, allowing homeowners to focus on cost-effective options or features that improve comfort without excess investment. Additionally, local codes or incentives can affect your selection, as some municipalities offer rebates for higher-efficiency installations or require compliance with specific environmental standards.
Evaluating Costs and Budget
Purchasing a furnace involves two distinct costs: the upfront expense of the unit and installation, and ongoing operational expenditures. High-efficiency furnaces are pricier initially but deliver substantial energy savings over their lifespans. Be sure to check whether there are state, local, or utility incentives for energy-efficient systems, as these can help offset higher purchase costs.
Exploring Advanced Features
Modern furnaces are equipped with innovations intended to refine household comfort and boost efficiency:
- Variable-Speed Blowers: These adjust the airflow rate, maintaining uniform temperature and minimizing sudden noise or drafts.
- Modulating Burners: These allow for multiple levels of heat output, resulting in more accurate room temperatures and energy conservation on mild days.
- Zoning Systems: Zoning allows homeowners to heat only the rooms in active use, making climate control both customizable and efficient for multilevel or large homes.
While these advanced options cost more upfront, they are worthwhile for anyone seeking premium comfort or aiming to reduce wasted energy over time.
Understanding Warranties and Service Agreements
A strong warranty and service plan can make a significant difference in protecting your furnace investment. Most manufacturers offer coverage for parts and labor on key components, but terms can vary. Service agreements, often offered by HVAC contractors, may include regular inspections, maintenance, and priority service if repairs are needed. This added cover helps homeowners avoid surprise repair costs and ensures the heating system runs optimally for years to come.
Consulting Professionals
A licensed HVAC contractor is an invaluable resource for selecting, sizing, and installing your furnace. Their expertise guarantees a system tailored to your home’s requirements and assures a safe, code-compliant installation. Having professional support from start to finish allows homeowners to access the latest technology, use warranties, and ensure seamless integration of new equipment into an existing setup.
Carefully assessing each aspect outlined above will put you on the path to finding a furnace that delivers reliable, energy-efficient, and cost-effective heating for your home, no matter what winter brings.